Identity theft is not a new problem and it has been around for a long time. Now, however, with most people moving their business online because of the world-wide pandemic, identity theft, especially online identity theft, has become an even greater problem.
In this article, we are going to discuss some important identity theft facts such as:
- What is online identity theft?
- Types of identity theft
- Why does someone want to steal your identity?
- How to protect your identity?
So, let’s get started by answering the first question.
What is Online Identity Theft?
Identity theft is, simply put, any fraud that is used to steal someone’s personal information. This includes:
- Your name;
- Usernames;
- Passwords;
- Email address(es);
- Phone number(s);
- Credit card information;
- Banking account information;
- Social Security number;
- Tax info;
- And more.
For scammers, all of this information is incredibly valuable and they will try to steal it in order to:
- Use the information themselves
They can either steal money directly from the account, make purchases over time, or use it for some other fraud.
- Sell the information
Today, criminals can buy and sell all kinds of info on the dark web and, naturally, this includes someone’s stolen data. For example, according to research done by Comparitech, the price for a stolen credit card on the dark web black markets goes from $0.11 to $986, while a PayPal account (hacked) goes from $5 to $1,767.
Okay, so you now know the “what” and the “why”, so let’s talk about the “how” online identity theft happens and what are:
7 Types of Online Identity Theft
Regarding the types of identity theft, there are several that you should be aware of both online and offline, such as:
- Medical identity theft
Personal medical records are extremely valuable and sought-after by scammers and, just to illustrate the point, nearly 231 million medical records were either stolen, lost, or exposed in a data breach in the United States alone between 2009 and 2019, according to Privacy Affairs research.
Items like medical insurance are particularly “interesting” to criminals and this can lead to an insurance application rejection, or getting bills for medical services you never had and even the validity of your medical records.
- Financial identity theft

Of course, when people think about identity theft, their biggest worry is that a criminal can use it to steal their money.
And, in most cases, this is the most common type of identity theft, online or offline.
Today especially, when almost all our data is connected online, and is easier to access (for example, you can pay bills or shop from a phone), it’s also become easier for cyber criminals to steal your information and access your financial accounts like bank accounts, credit card info and so on.
In addressing identity theft challenges, it’s crucial to carefully review and enhance the systems that protect your personal and financial information. An essential part of this strategy involves the careful selection of reliable tools.
Compare credit card providers to find those that offer the strongest safeguards, effectively reducing the risk of unauthorized access and ensuring your data remains secure. This approach helps to reinforce your defenses against potential security breaches.
- Email address change
Having your email address changed unwillingly is a two-pronged problem.
Not only can the criminal see your personal or business correspondence, but they can also redirect your incoming mail to a different address that they control and with that obtain sensitive and valuable information.
- Employment identity theft
According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, the unemployment rate in the country for February 2021, was 6.2%, which is the lowest since April 2020 when it was at the highest since the Great Depression at 14.8%.
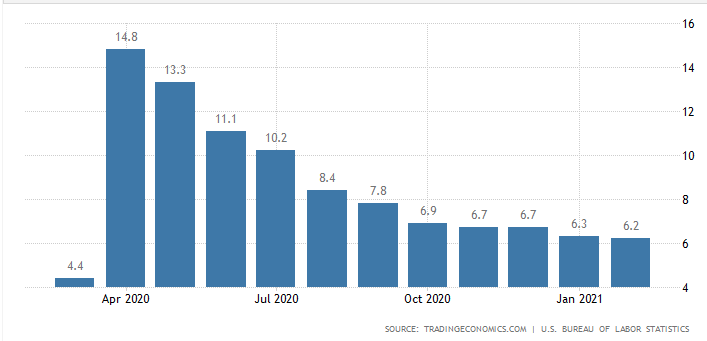
Source: https://tradingeconomics.com/united-states/unemployment-rate
Yet, despite the unemployment rate getting lower and being below the market expectations (6.3%), there are still millions of unemployed (just below 10 million).
A lot of businesses had to make cuts or even shut down due to the Covid-19 pandemic, leaving many jobless and this has led to a hike in employment identity thefts, especially among groups who want to avoid background checks and are using someone else’s SSN.
- Online account identity theft
Online account identity theft can either mean a takeover of an existing account, or the creation of a completely new account, using the victim’s stolen information.
If your existing account gets stolen, this enables the hacker to transfer funds to their account, make credit card changes, order and pay for things from your account, etc.
However, it’s relatively easy to spot if your account is breached by simply noting if there are any changes to it that you haven’t made.
That’s why a lot of scammers use a different strategy, that is less obvious, and that is to create a new account using your information.
This, for instance, can negatively affect your credit record, so if your credit score has suddenly dropped for no apparent reason, it might be because you are a victim of identity theft and someone has created an account in your name.
- Children identity theft
Children, alongside the elderly, are the most high-risk group for identity theft according to LifeLock and in 2019, 1 million U.S. children were victims of identity theft.
This is because people often pay less attention and effort to monitor and protect children’s accounts than they do their own believing that there’s no money to steal and they would therefore not be of interest to criminals.
This is wrong. Criminals can use a kid’s Social Security number to apply for a mortgage or a credit, making it easier for them to get it.
The bigger problem is that children identity theft can go undetected for years, until the kid applies for a school loan itself and it gets rejected or you receive a tax notice, or you are declined government benefits.
- Inheritance identity theft
Unfortunately, the dead are not safe from identity thieves either.
One example of this is when a criminal steals a deceased person’s identity and uses it to apply for loans, receive government benefits, empty the deceased bank account and so on.
Naturally, as this strange activity from a deceased person gets picked up, this can also affect the family.
What are the Most Common Online Identity Theft Methods?
Scammers use different methods to commit online identity theft. Among the most common are:
- Phishing
Phishing is still one of the biggest problems online and the favorite tactic used by scammers to obtain a person’s sensitive information by pretending they are from the government, bank, or another legitimate business or institution.
The “classic” version of phishing involves a scammer sending phishing emails to a large number (often thousands) of email addresses, but since people have become wise to it, scammers have started using a more targeted approach like spear-phishing, with higher success.
- Pharming
Pharming is similar to phishing, but with a few notable differences. The biggest is that, in a pharming attack, the victim is redirected to a fake website without knowing, whereas,in a phishing attack, they are “tricked” into clicking a link.
Once on the pharming website, the unsuspecting victim might leave their information, exposing them to the hacker.
- Remote access
This is one of the more famous online scams and it involves the scammer (often from India) calling the victim and pretending to be tech support from a computer or telecom company and convincing them to install a remote software on their computer in order to “solve the issue”.
Once the scammer has remote access, they will point to different “error” messages (mostly created by themselves) and will try to convince the victim into purchasing some malware-ridden software to “fix it” and to send money to their account as “payment for their services”.
- Fake online profiles

Since people don’t use email that often in personal communication, but more social media, scammers have naturally picked up on that as well.
This works similar to email phishing, only this time, instead of using the email, the scammer creates a fake social media profile and pretends to be working for a bank or an insurance company.
From this profile, the scammer then proceeds to send messages to people about fake bank or payment issues, which contain links or attachments with malicious software in them.
How to Protect Against Online Identity Theft?
So we answered, what is identity theft, why it happens, how it happens, what are the most common types and methods, but now the question is:
How to protect against online identity theft or scam?
First of all, if you or someone you know is a victim of identity theft, you can report this at FTC identity theft if you are a U.S. citizen.
- Click on the “Get Started” button

- On the next page, select the statement that best describes your situation, i.e. type of identity theft.
For instance, you can report that someone has filed a Federal tax return in your name, used your info to file for unemployment insurance, report another type of identity theft, or that someone else has your information that you are worried about.
- Follow the prompts on the next page to report the identity theft.
Of course, while it’s good to know what to do in case identity theft happens, it’s even better for it not to happen at all. To protect yourself from identity theft:
- Be mindful of phishing scams
Phishing is the tried-and-true method for scammers to steal their victim’s data online, so it’s important to know how to recognize a phishing email.
The most important thing here is to avoid clicking on any suspicious links.
- Use strong security, anti-malware and antivirus software
It’s much easier for a criminal to enter a weakly-secured house that has no security lock, cameras, alarms or motion sensors, than the one that has these things.
The same goes for your devices. If you are using software that hasn’t been updated in a while and has no malware or virus protection, you are just making things easier for the hacker.
- Never provide sensitive information over email, phone, or social media.
If someone asks you for your personal or financial information over email, phone, or social media, don’t respond. The institutions that do actually require this information will never use these to ask you for them.
- Regularly check and monitor your bank accounts and credit card
If you haven’t already, be sure to enable alerts and notifications from your bank or credit card providers to know of any changes that happen on them.
For example, I receive an SMS notification and an app notification every time I use my card, so I would immediately know if someone else has used it.
- Keep your SSN safe
The Social Security number is one of the most important pieces of data that you have and is, as such, the most targeted by criminals.
That’s why you need to keep it safe.
Never send or share your SSN over email and avoid storing it on your smartphone or laptop.
- Only buy stuff from reputable websites
If you’re doing a lot of online shopping, you should know by now that there are reputable and “reputable” websites.
For instance, reputable shopping sites would be Amazon, eBay, Ali Express and the like, so buy from such sites only.
How to protect yourself from identity theft?
To protect yourself from identity theft, you first need to be mindful of the different scams that criminals use to steal your information, like email phishing. Also, avoid giving out your information to suspicious requests and keep your data secure by using anti-malware and antivirus software and the latest security updates for your software.
What to do about identity theft?
If you become a victim of identity theft, be sure to report this to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), your bank and credit reporting companies.
Also, if a purchase has been made with your stolen credit card on a website, try contacting the site to stop the order and receive a refund to your card.
If necessary, contact the police and freeze your credit.
Conclusion
Online identity thefts and scams are nothing new, but in recent years, they are only getting bigger and meaner. According to Cloudwards, 1 in 15 people in the U.S. have fallen victim to identity theft and 1 in 4 identity theft victims experience a second or repeat identity theft.
One of the most common targets for identity thieves and scammers is your email. Having a secure email that will keep the data you send and receive is imperative and using a secure email service will help you with that.
One such email service is CTemplar: Armored Email, so if you are looking for a secure and encrypted email provider, check out CTemplar.