Worst Cybersecurity Risks on the Darknet
However, to access the dark web, you will need special software called Tor. Tor is a free software available for download at Tor Project that allows you to communicate anonymously online. We explained in one of our previous articles whether Tor is completely anonymous to use, so check that article as well.
Before you do that, you should know of the different types of cybersecurity attacks on the Darknet and of the other cybersecurity risks that await you on it.
Types of Cybersecurity Attacks on the Darknet
The Darknet can be an inviting place for one looking for anonymity on the Internet, but it’s far from a place where you should wander carefree. Many cybersecurity risks are lurking behind every corner and nook of the Darknet.
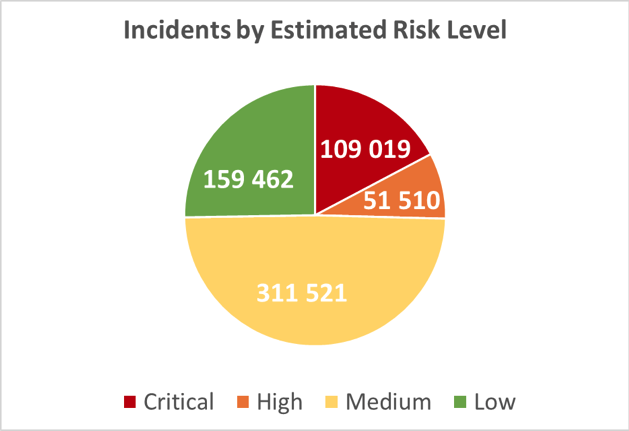
In fact, in a State of Cybersecurity Industry Exposure at Dark Web report from September, 2020, ImmuniWeb found that out of 398 cybersecurity companies from 26 countries, 97% had their data exposed on the Darknet and, out of 631,512 cybersecurity incidents found, 109,019 were classified as “critical risk level” in the report.
So what are the different types of cybersecurity attacks on the Darknet that you could expose your data to if you are not careful?
Phishing
Not much different from the surface web, phishing and all its subspecies, like whaling and spear-phishing, remain one of the biggest threats on the dark web as well.
Of course, when we are talking about phishing, it’s important to distinguish the different types of phishing attacks such as:
- Regular or deceptive phishing, in which the scammer will impersonate a legitimate organization to get your data;
- Spear-phishing, where the attack will specifically target a specific company, organization, or individual;
- CEO fraud or Whaling is a phishing attack that goes after the “big fish”, like the CEO of the company or other high-end exec.
To this, we can also add another type of Internet scam that is similar to phishing, pharming. However, don’t confuse phishing and pharming. The biggest difference between phishing vs pharming vs spear-phishing is that both phishing and spear-phishing use some kind of “bait” to lure the victim, whereas pharming does not use a bait.
In a typical phishing attack, the victim receives an email that looks like it came from a legitimate brand and is lured into clicking a link to a malicious website or page, where the criminals can steal the victim’s personal or financial data, login credentials, etc.
Pharming works a bit differently in that it doesn’t use a bait. Instead, the victim is unknowingly sent to a pharming website. The reason that the user will most likely be unaware of being “pharmed” is that their address bar will actually show the same URL for the pharming website as for the real website. That is because the hacker was able to corrupt the DNS server itself.
You can see the differences between phishing and pharming in the next table:

Identity Theft
According to Javelin Strategy & Research, 13 million consumers were victims of identity theft in 2019 alone. The total cost of these was $3.5 billion.
What is identity theft?
Identity theft or identity fraud is any type of crime in which a criminal obtains the victim’s personal data and uses them for economic gain.
This can be as simple as someone looking over your shoulder as you write your name or type your credit card number, to getting the scammer getting the victim to reveal their data for some promised benefit, which they never intended to keep (but keeping the data).
When it comes to the different types of identity theft, some of the most dangerous are:
- Tax identity theft
In a tax identity theft, the fraudster will try to use your personal info to file a tax return and collect a refund.
One of the most common ways criminals can obtain your personal and tax information for a tax identity theft is by pretending to be from the IRS. Of course, the IRS will never ask for your private information over email or phone, so if you believe you’ve been a victim of a tax identity theft, you should report the instance to the IRS.
- Medical identity theft
Millions of Americans are victims of medical identity theft every year. According to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), medical id theft jumped 101% from 2018 to 2019.
In a medical identity theft, the fraudster will pretend to be another person and use their stolen information to avoid paying their medical bills.
The danger here is not only financial, but also in the fact that your medical history will be mixed up with that of the fraudster, which might lead your doctor to make a wrong diagnosis or prescribing you wrong treatment.
- Social security identity theft
SSN or Social Security Number is one of the prime targets for identity theft by criminals online. If a criminal is able to obtain your SSN, they can open a fraudulent account in your name and negatively affect your credit score.
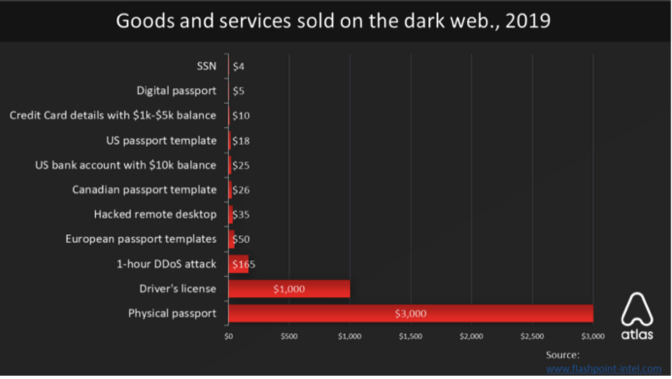
On the dark web, stolen (often fake) social security numbers go for about $1-4 apiece according to AtlasVPN.
- Card fraud
Card fraud involves debit and credit card fraud and this occurs when someone uses your card without your authorization.
To do this, a criminal doesn’t even need your physical card. If you’ve been making purchases on unsecured websites, a criminal might be able to see your card number, security code and PIN and use those to make transactions of their own.
A lot of online markets on the dark web are not safe to use because of this fact. A lot of Darknet vendors will only create a marketplace to fraud unsuspecting people out of their money or bitcoin. This is called an “exit scam”.
One such case happened in 2012 when the admins shut down the dark web marketplace Evolution without warning their buyers and making off with $12 million in BTC.
- Mortgage fraud
In case of mortgage fraud, if someone manages to steal the homeowner’s SSN or their mortgage account number, they would be able to take a second mortgage on the homeowner’s property or a home equity line of credit and elope with the money.
What if your email ends up on the dark web?
If that happens, immediately scan your computer for possible malware, change your email password once you get rid of the malware, start using multi-factor authentication, start using more than one email account and stay away from data brokers and people search sites.
Spoofing Attacks
Another type of cybersecurity attack that you might encounter on the dark web are spoofing attacks.
What is a spoofing attack?
A spoofing attack is an attack in which the intruder attempts to imitate a legitimate user or a device to launch an attack against a network.
There are several types of spoofing:
In this case, the attacker will send an email masquerading as an admin or support for a service or website that you are already using to trick you into resetting or revealing your password somehow.
- IP spoofing attack
With IP spoofing, the hacker will impersonate another user’s legitimate IP address by sending packets from a fake source address and then send these packets to different devices in the network, until eventually clogging the network, similar to a DoS attack.
- DNS spoofing attack
The DNS spoofing attack mixes up public IPs and modifies domain names, which it then re-routes to new IP addresses and sends users to spoofed domains.
- MAC spoofing attack
When it comes to MAC spoofing, the hacker can’t change the MAC address, but can instead create a fake one and use it from a rogue device to perpetrate attacks.
- ARP spoofing attack
This type of spoofing attack only works if you use the ARP protocol on your LAN network. Basically, the hacker will send ARP messages throughout the network looking to connect their MAC address with the IP address of someone in that network in order to hijack the data between their computer and the router.
- Biometric spoofing attack
A biometric spoofing attack involves the criminal somehow getting into possession of a victim’s biometric, like a fingerprint and using it to trick the device.
In an age when a lot of mobile users use biometrics instead of passwords to access their devices, biometric spoofing attacks can be very dangerous.
For example, in one research, it was shown to be possible to trick facial recognition systems using a 3D render of a person’s Facebook photo.
While facial recognition relies on authentic imagery, deceptively created 3D modeling can now fabricate convincing doppelgangers to compromise security protocols seeking matches.
Just as renders synthesize fabricated environments, hyper-realistic portrait rendering allows misinformation tactics to circumvent safeguards trusting camera footage as fact rather than manipulating fiction.
As computer-generated personas and deepfakes call truth itself into question, even AI struggles to detect exceptionally created 3D modeling mimicking real biometrics with eerie precision to dupe digital defenses.
Though no model is perfect, today’s accessible rendering software empowers hobbyists to craft identity theft tools by created 3D modeling uncanny resemblances, warranting upgrades to distinguish legitimate users from criminally engineered artifices.
- DHCP spoofing attack
In a DHCP spoofing attack, the attacker will use a rogue DHCP server to send out fake DHCP responses to one or more devices on the network, replace the IPs of a Default Gateway and DNS server and re-route the traffic to a server they control.
Identifying Darknet Cybersecurity Risks
According to an IBM study, the average time it takes to identify and contain a cybersecurity breach is 280 days and the average cost of a data breach is $3.86 million.
As businesses confront the complexities of the dark web’s obscure territories, it’s imperative for them to undertake detailed risk assessment processes.
This strategy is vital for detecting and sequencing security vulnerabilities, enabling the strategic application of focused protective actions. Tailoring these assessments to meet the distinct dangers tied to the dark web markedly amplifies an organization’s defense mechanisms.
By adopting such a forward-looking approach, a company not only fortifies its defenses against digital intrusions but also enhances its ability to respond swiftly and efficiently to these challenges.
Deepnet and especially Darknet, often pose an even bigger challenge, but using context-rich threat intelligence it is possible to detect and avoid a specific cyber risk you or your company might be exposed to on the dark web.
There are several ways you can do this:
- Industry or Organization Discussion
One of the first cybersecurity risk factors you should look into are mentions or discussions of your company’s name or your industry or vertical on the dark web forums, chat rooms, or paste sites.
Using contextual analysis you can determine if a hacker already has your data or if they are planning to steal it.
- Lost or Stolen Credentials
A Verizon report from 2017 revealed that lost or stolen credentials (usernames and passwords) account for 22% of data breaches.
A great tool to discover if your password has been revealed is called Have I been Pwned.
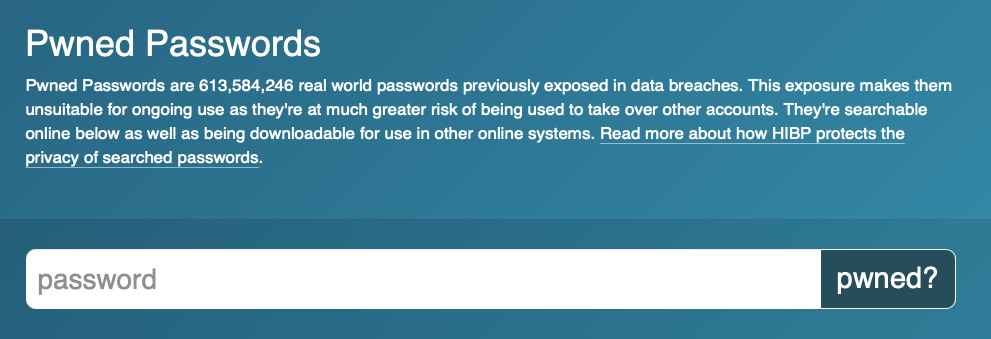
The question that contextual analysis needs to answer if your credentials have been compromised would be was this a recent event or data from an earlier data breach?
- PII Exchange
Personal identifiable information is any information that can identify a person, whether alone or in conjunction with other data.
In that regard, we can separate two types of PII:
- Sensitive (your name, SSN, medical records, financial information, driver’s license…);
- Non-sensitive (your gender, date of birth, race…).
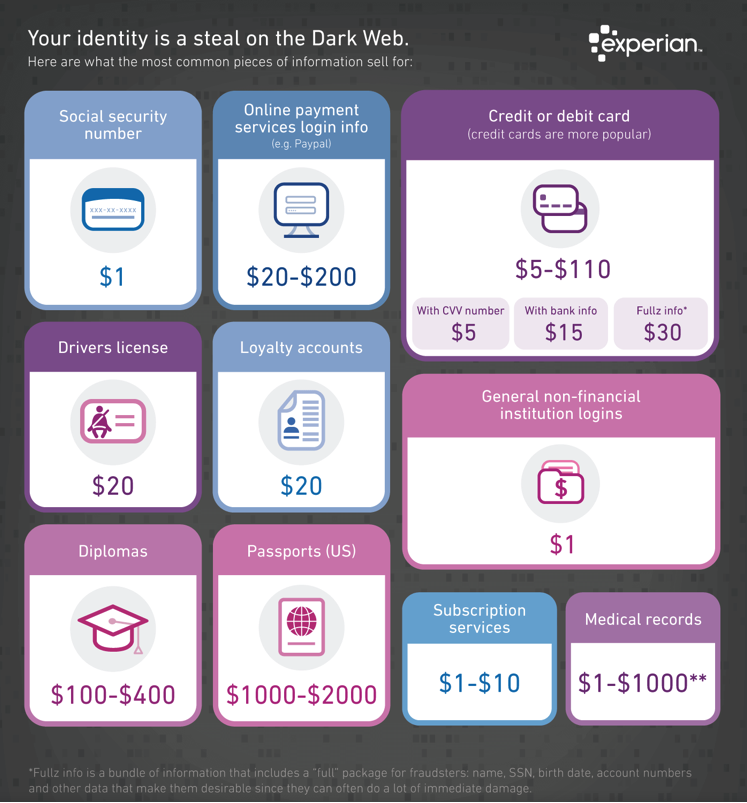
There is a huge market for stolen PII and, depending on the type, your sensitive data can go from $1 for a social security number to $1,000+ for complete medical records, according to Experian.
- Phishing Attack Coordination
With phishing-as-a-service kits now available to anyone on the dark web for just a few bucks, phishing has become much more “accessible” to criminals who until now lacked the know-how to create phishing software of their own.
Luckily, this also means that you can familiarize yourself with PhaaS kits to better educate and prepare yourself and your users.
- Trade Secret Discussions
Another cybersecurity risk you should pay attention to on the Darknet is trade secret discussions. For a company that has its trade secrets and other sensitive assets stolen, the cost can be substantial, both financially and in reputation. This is why it’s vital to know this ahead of time.
What is a cyber attack?
A cyber attack is any attack perpetrated by cybercriminals against a computer or network, usually to steal data, disable the system, or to use the now compromised computer to launch more attacks.
What do cyber terrorists attack?
Cyber terrorists and other threat actors can go for a variety of targets from an individual and his PII, an organization’s data and trade secrets, to a country.
How to protect against cyberattack?
Never share your sensitive data, use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, keep all your software up-to-date and use software that is designed for security and privacy over those that aren’t (CTemplar over Gmail for instance).
What to do after a cyberattack?
If you’ve been a victim of a cyberattack, first determine the magnitude of the attack and what was compromised. Make sure to change your passwords and access permissions immediately. If there is any information posted online, attempt to remove it from websites where it might have been posted. Finally, revise and update your current cyberthreat plans.
How to prevent a cybersecurity attack?
Preventing a cybersecurity attack is much less costly than reacting to it once it already happened. There are several ways to prevent a cyberattack in your organization:
1. Ensure better access control to your systems and network;
2. Ensure endpoint protection;
3. Step-up employee cyber security training and education;
4. Keep software up-to-date;
5. Backup your data.
The recent privacy policy changes that WhatsApp announced have once again opened up the discussion about privacy on the world wide web and just how little large Internet companies like Facebook (WhatsApp’s owner), Google, Apple, Amazon, or the like care about user’s privacy.
You might have already switched from WhatsApp to an end-to-end messaging app like Signal, or from Gmail to an encrypted email service like CTemplar, but now you are looking to take a step further and start using the Darknet.
Conclusion
The Darknet can be useful to anyone looking to be anonymous. Unfortunately, people might seek to remain anonymous because they have criminal intentions. Hopefully, this article will give you the edge to deal with these threat actors.
If you are looking for a secure and anonymous email service that you can use over Tor, try CTemplar.
To further enhance your digital privacy, learning how to remove your PII from the internet is crucial. This step minimizes the risk of identity theft and other cybersecurity threats by ensuring your personal information is not easily accessible on public platforms.
You can visit us at our official .onion address.