Telling a human face is a core social skill and one that we developed throughout our evolution. But not everyone is as good at it which makes facial recognition done by humans spotty at best.
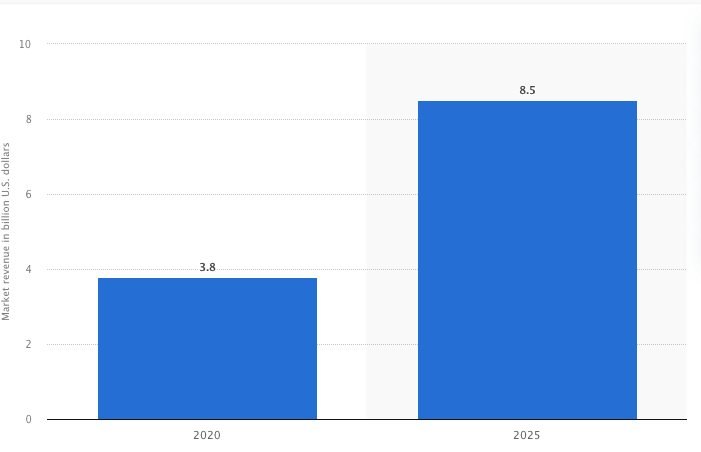
In recent years, facial recognition technology has seen a surge as the market size is expected to grow from $3.8 billion in 2020 to $8.5 billion in 2025 according to Statista.
However, even though facial recognition technology has numerous applications from aiding law enforcement to stopping toilet paper thieves (apparently, that’s a thing in China), opponents of face recognition technology often voice their concern about how it affects our privacy.
What is Facial Recognition Technology and How Facial Recognition Works?
Facial recognition is the process of recognizing human faces (or in some cases animal) using technology to match the biometric features from a photo or a video with the information in the database.
While each face recognition system works slightly differently, the basics of it are not much different from how we normally do it when we meet someone.
We see a person, hear their name and next thing our brain “stores their face” along with correlating information (Bob = big nose, Anna = blue eyes) so that next time we see that person, this “information” is pulled out from our internal database (that is, your brain) and we go “Hi Bob!”
Of course, facial recognition technology works on a more grander scale (we can remember between 5,000 and 10,000 faces) since it draws from artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Here is how facial recognition works:
- First, your face is captured in a photo or a video, for instance, by security cameras, alone or in a crowd, looking straight (or nearly straight);
- Next, the facial recognition software analyzes the biometric features of your face, the distance between the eyes, jaw width, forehead width, etc. (there are 68 facial landmarks) to create a face signature;
- The face signature is then compared to the database of known human faces to find a match. More than 115 million Americans have digital images of their faces stored in one or more police databases. Additionally, there are also free facial image datasets (Google Facial Expression Comparison for example contains 156,000 facial images and there’s even a Simpsons facial database);
- Finally, the software matches your faceprint with the image in the database.
Where is Facial Recognition Software Used?

Facial detection technology has different applications, including:
- Helping police department to identify suspects and track criminals;
- Controlling access to sensitive locations such as bank vaults;
- Finding missing children and adults;
- Tracking attendance (in school or church for example);
- Protecting retail businesses from thieves;
- Diagnosing certain diseases;
- Identifying people on social media;
- Unlocking mobile phones;
- Advertising;
- Protecting schools from threats such as drug dealers, expelled students, etc.;
- Detecting cheats at a casino;
- Expedite secure transactions;
- Replacing keys in automobiles;
- Confirming identity at ATMs;
- Finding lost pets;
- Controlling how much toilet paper you can take.
Why Facial Recognition Software is an Issue for Your Privacy?
Look around you and you’ll see facial recognition cameras everywhere, from your local supermarket, the bank, the school where your kids go to, all the way to the street and your own phone.
How much control do you really have over your biometric data? One has to take into account how facial detection technology affects their privacy and security.
- Where can your facial signature end up? With this technology now everywhere, do you even know who has access to those surveillance cameras?;
- How good is facial recognition security? Again, your image can be stored in a database with or without your permission (usually without). Is it safe from hackers?;
- Is it accurate? Facial recognition algorithms are not 100% accurate. In 2020 a black man in Detroit was wrongfully arrested because the facial recognition software mistook his identity for someone else’s;
- Who “owns” your face? Of course, no one can “steal” your face (Jaqen Hgar style), but once the digital image is in the facial recognition system it can be used to track you down or even sell your biometric data to the highest bidder without your permission;
- What about your freedom? Shouldn’t what we do and where we go sometimes be private (most times)? If law enforcement, government agencies, Google, Facebook and others can track you at will, you can say goodbye to your private life.
Facial Recognition Security Best Practices
Being a relatively new technology, it’s important to know both the pros and the cons of facial recognition. For many organizations, it provides huge benefits, but there are also risks in letting the AI recognize faces without any constrictions.
For this reason, wherever facial recognition or other biometric technologies the following best practices should be observed:
What are biometric technologies?
Biometric technology is the use of technology to identify people based on their physical and biological characteristics such as fingerprint, iris, face, handprint, voice, etc.
- Affirmative Consent – Always get affirmative consent when introducing someone into a face recognition system or identifying them to a 3rd-party that would not have known their identity;
- Full Transparency – Let your consumers and visitors know that you’re using facial recognition technology and, more importantly, how their data is used, where is it stored, how it’s maintained and with whom it is shared;
- Take Good Care of Facial Recognition Security – The data that face tracking technology collects (namely, the digital image of your face) is highly sensitive and personal information and therefore those who collect it should have strong administrative, physical and technological safeguards to protect the privacy and security of it;
- Consider the Purpose – Why are you collecting this data? Only use biometric technology such as face detection if you have a reasonable context to collect, store, maintain, share and use this data;
- Right to Correction and Deletion – People should have the right to request access to their data (including their photos in your database). They also ask for correction and deletion, especially where the software has mislabeled their identity or they want to prevent their sensitive information to get sold;
- Take Full Accountability – Finally, be sure to take full accountability as to how your company uses facial recognition data and how it shares it with 3rd parties.